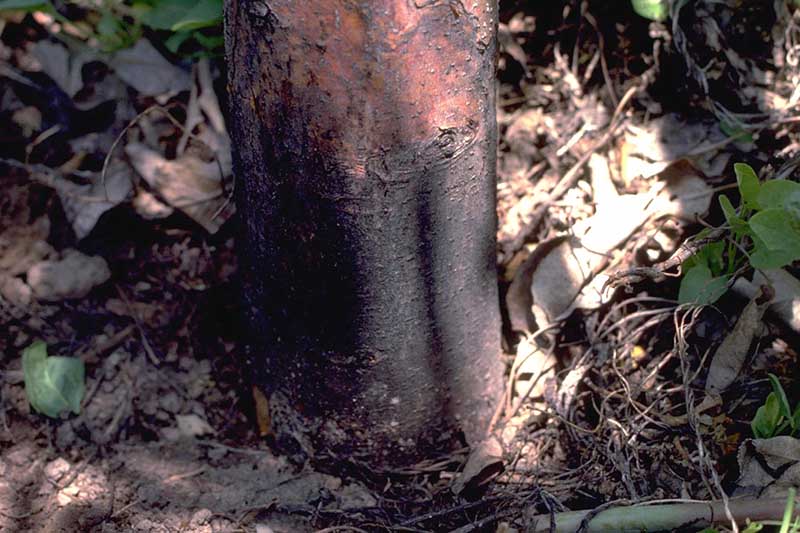
How to Identify and Treat Pecan Stem End Blight
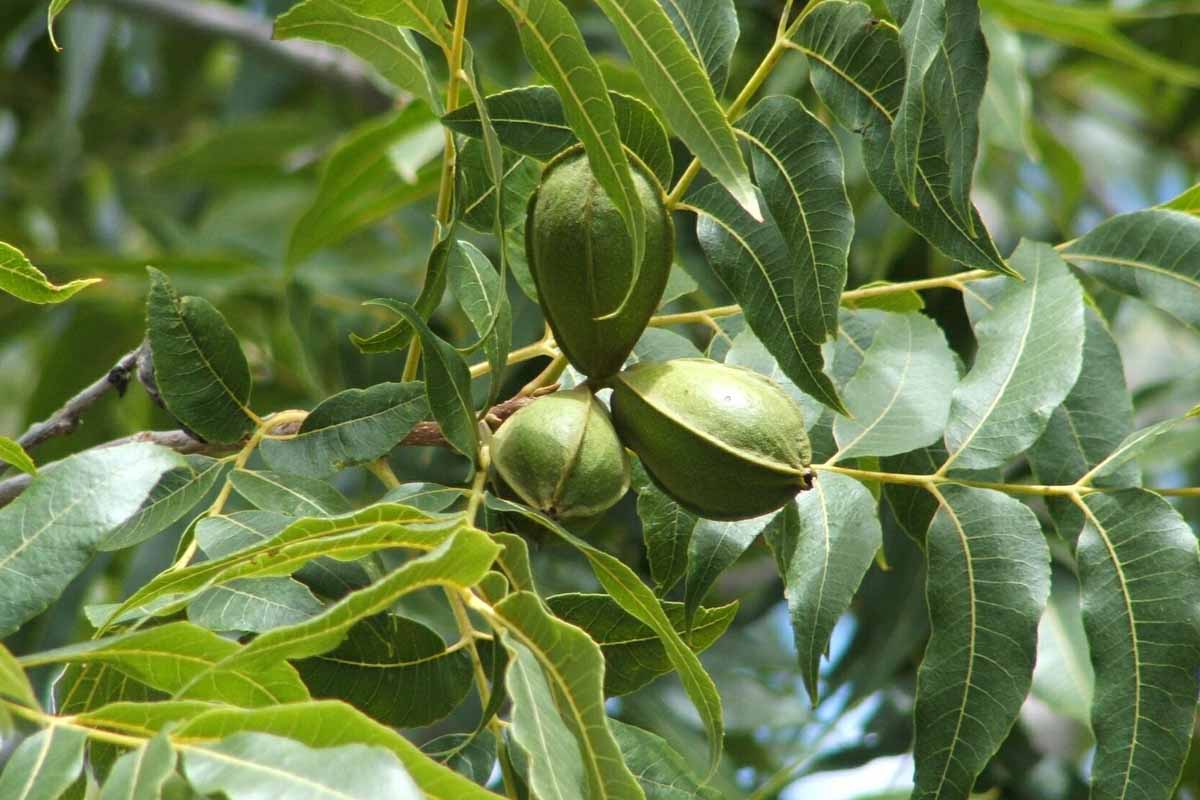
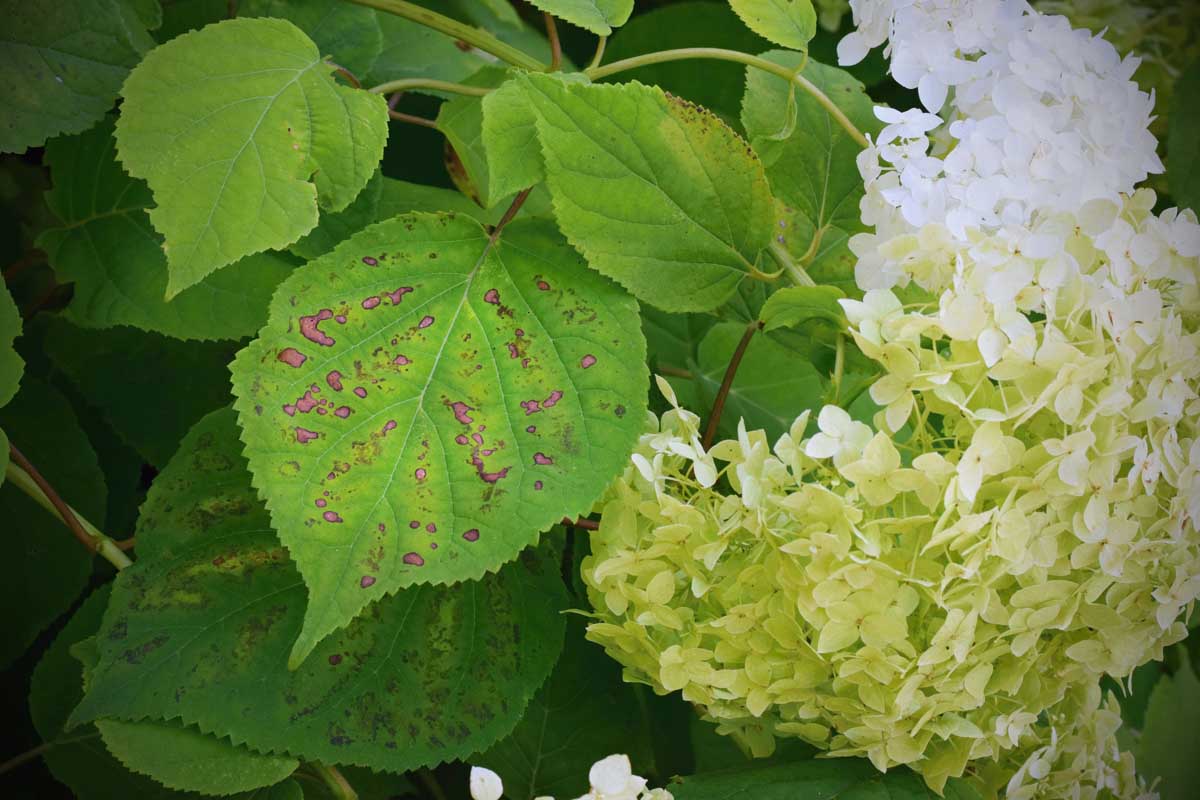
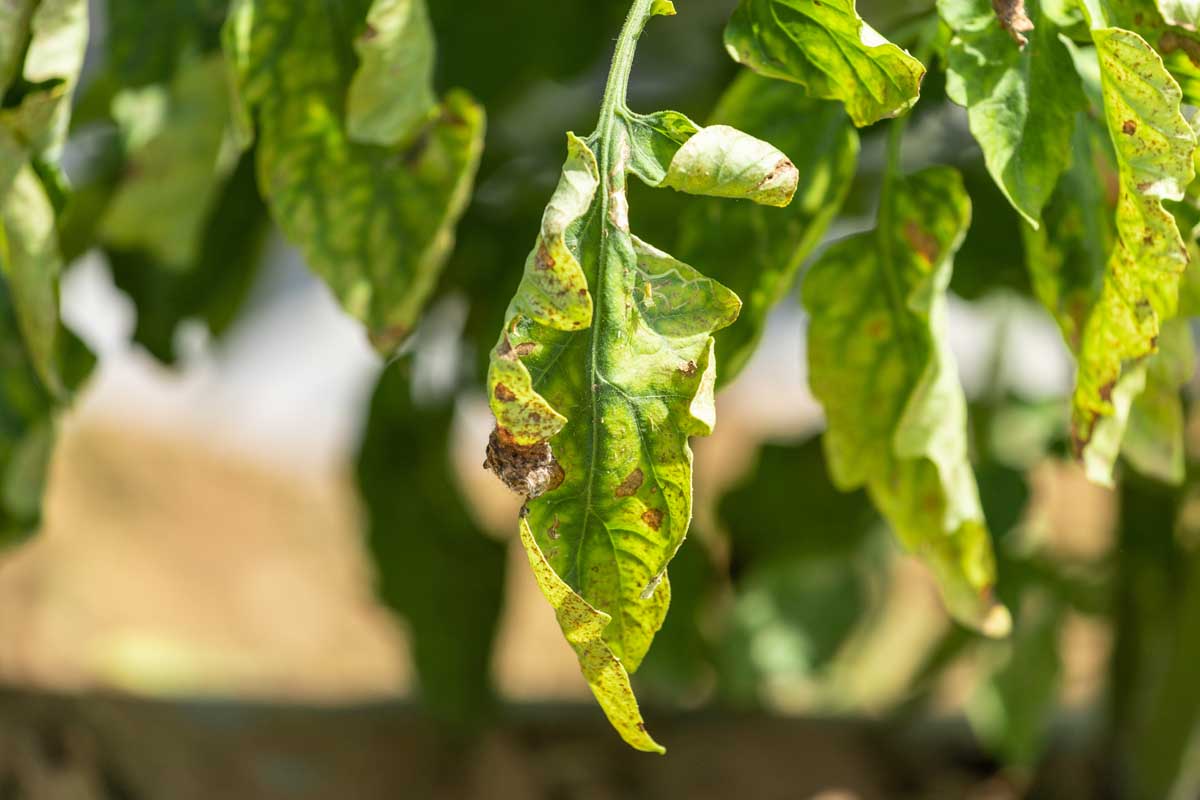
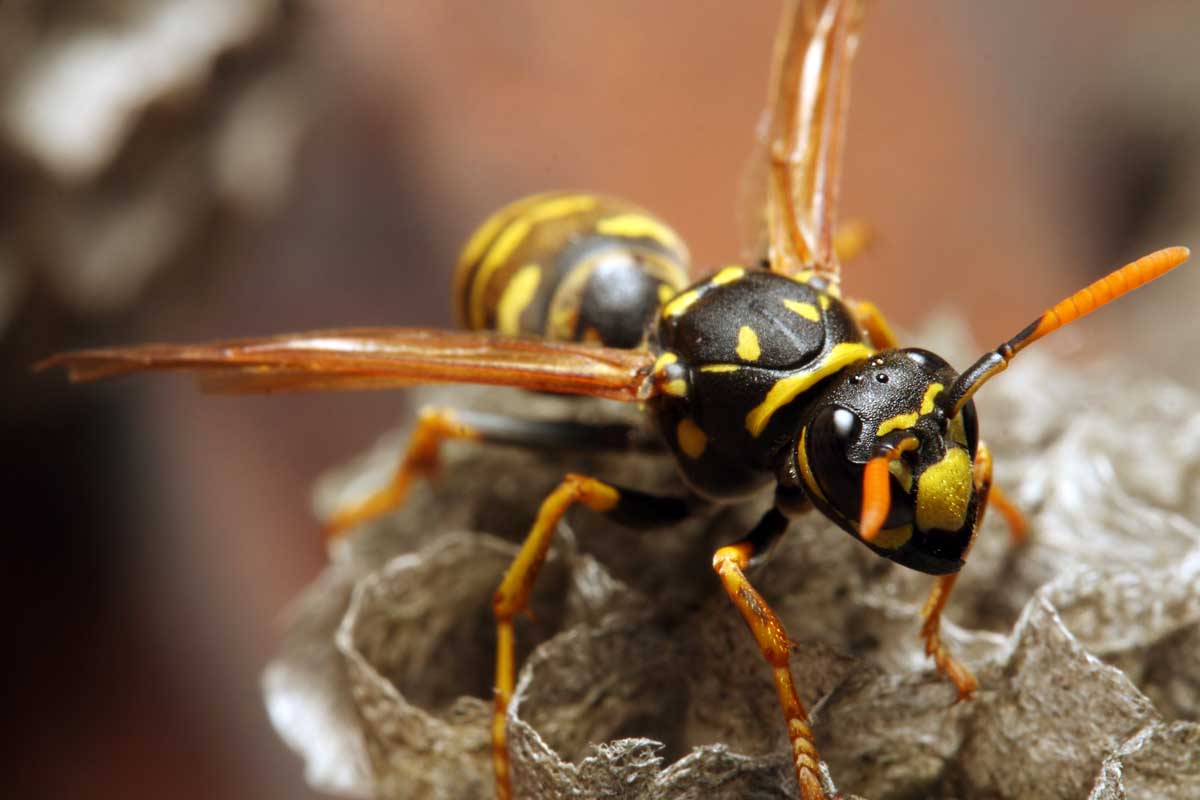
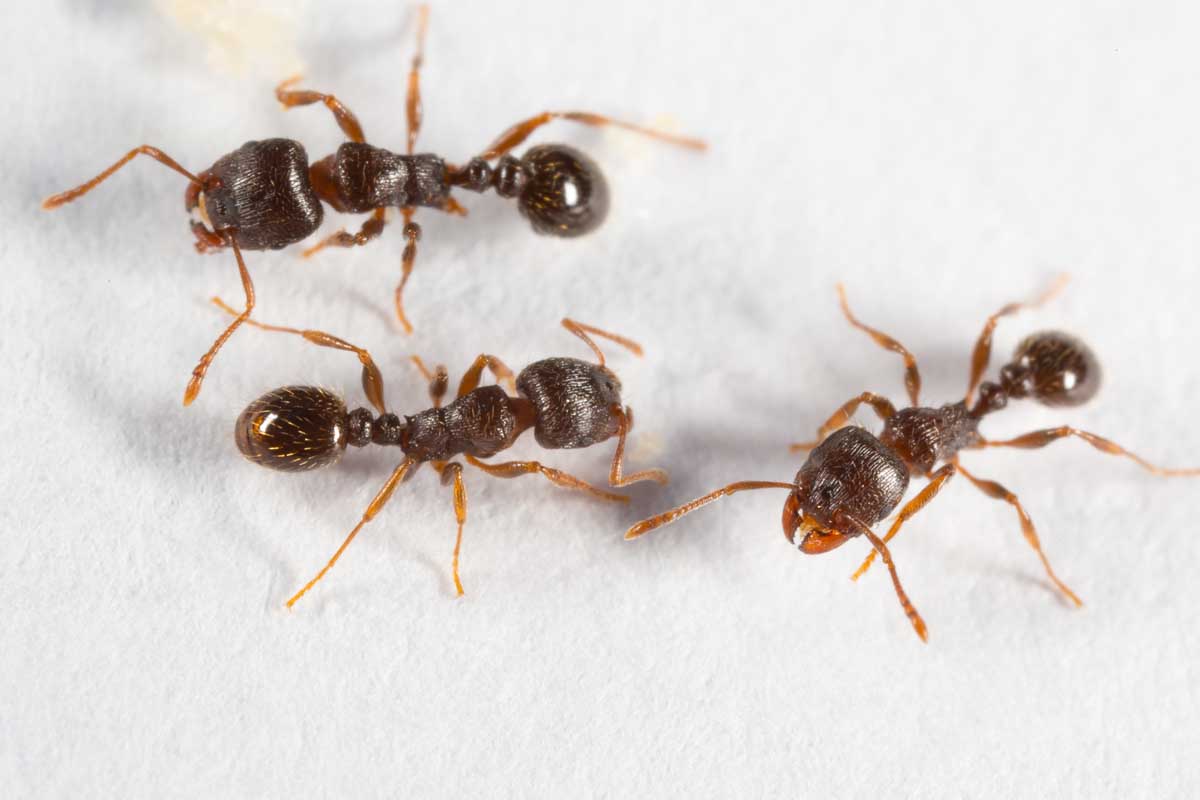
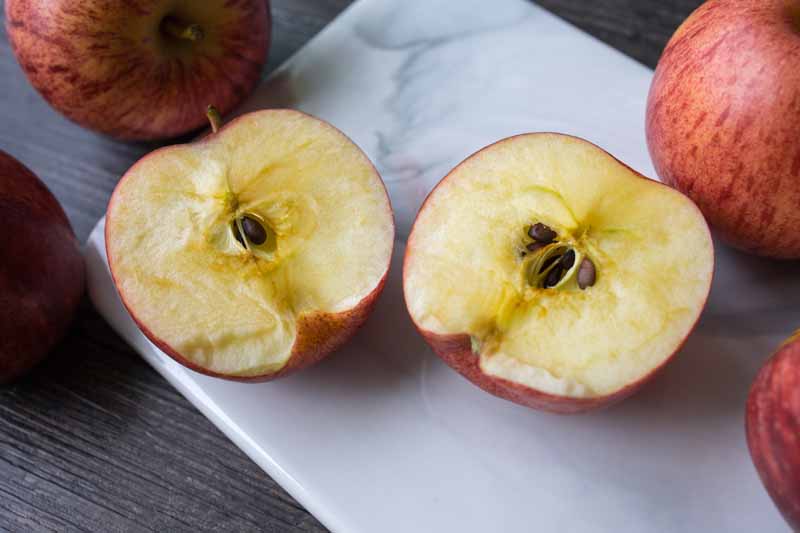
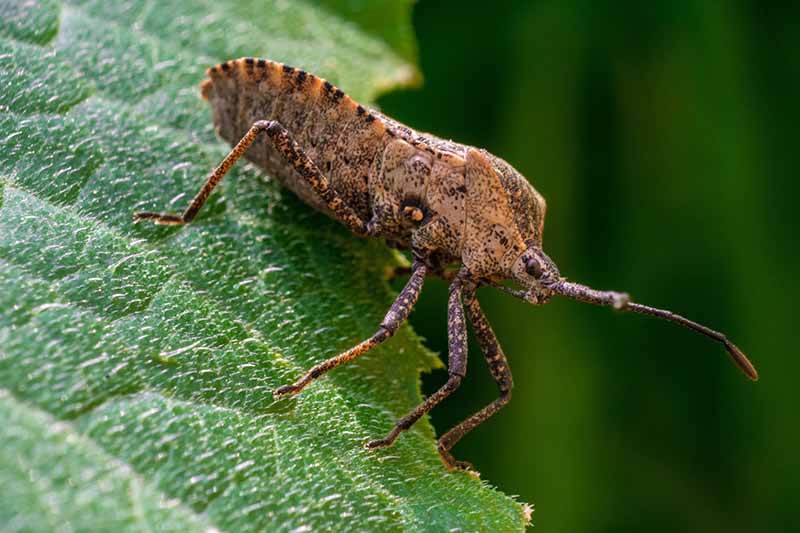
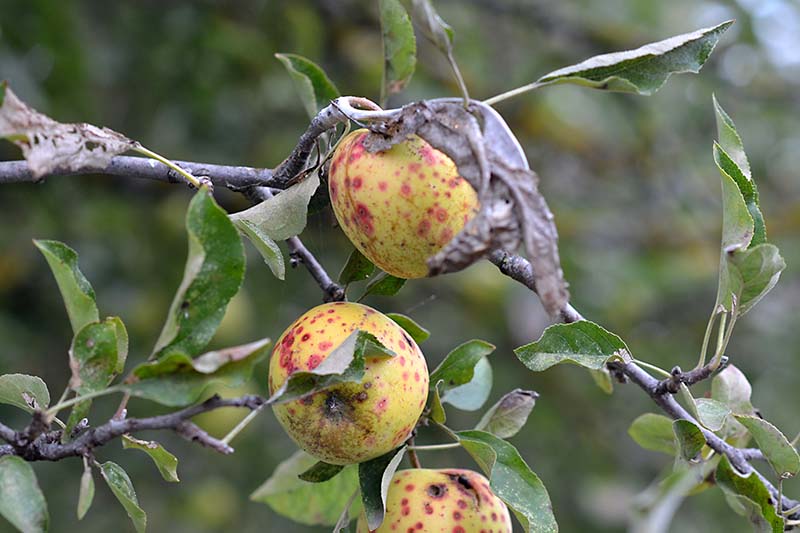
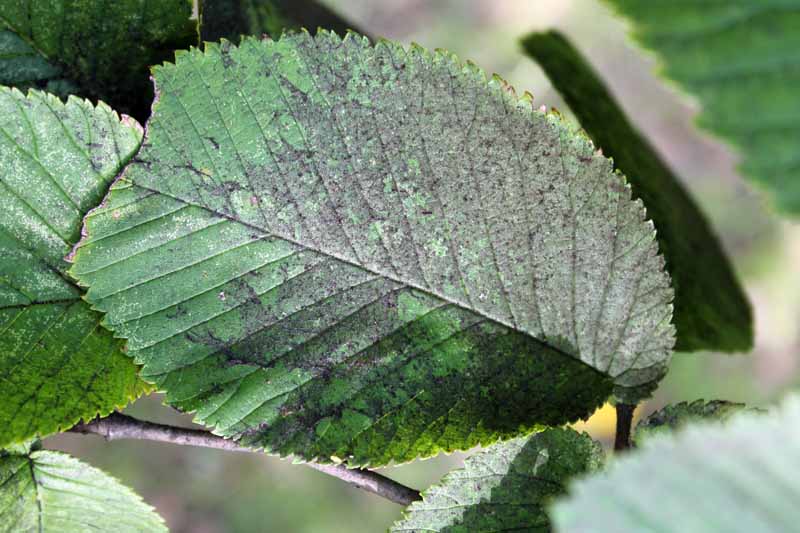
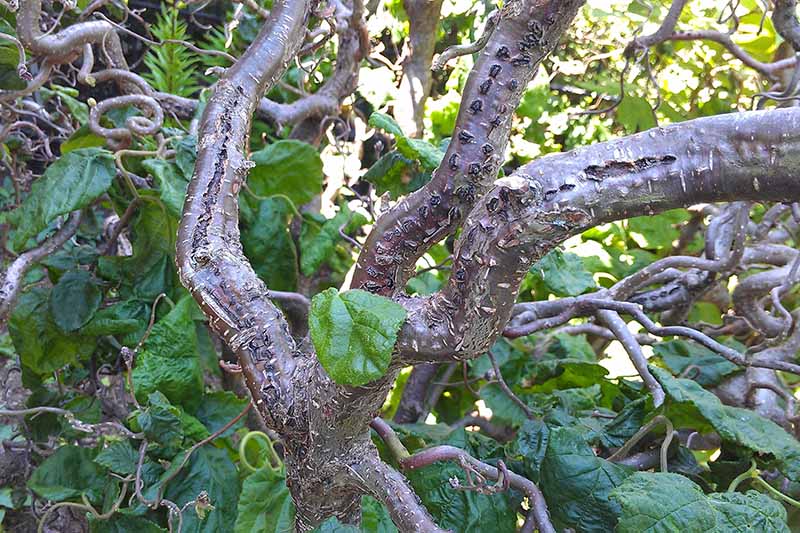
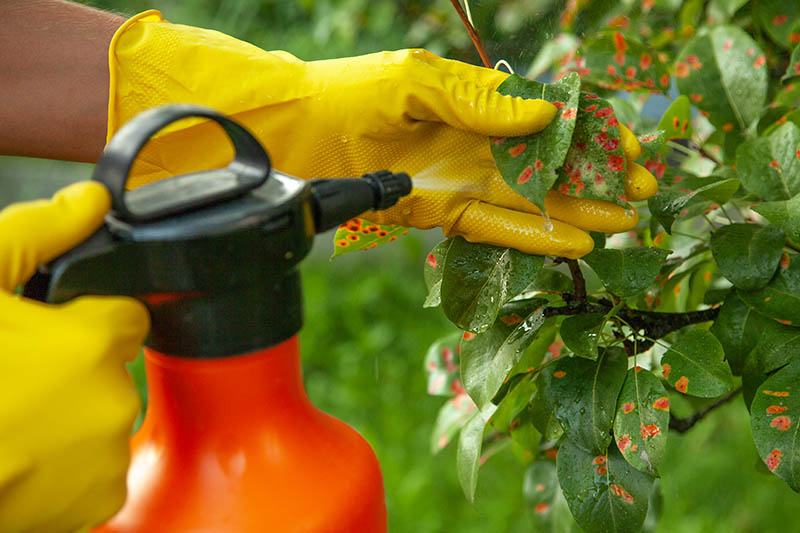
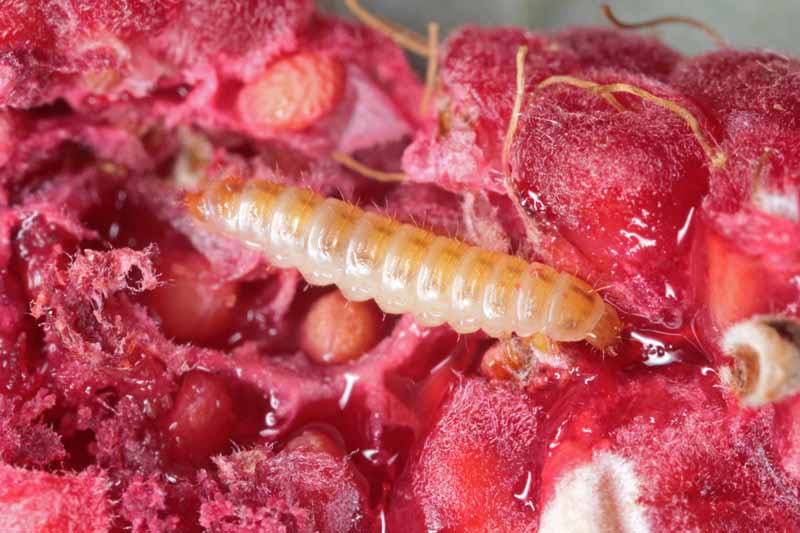
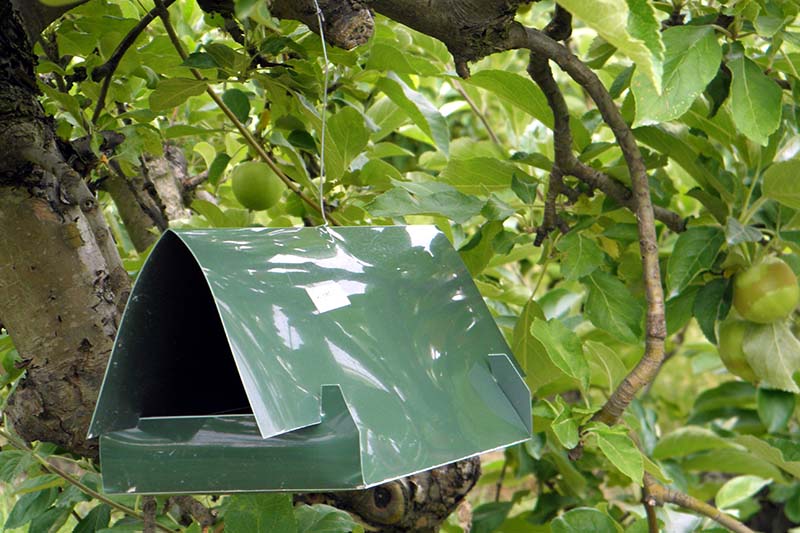
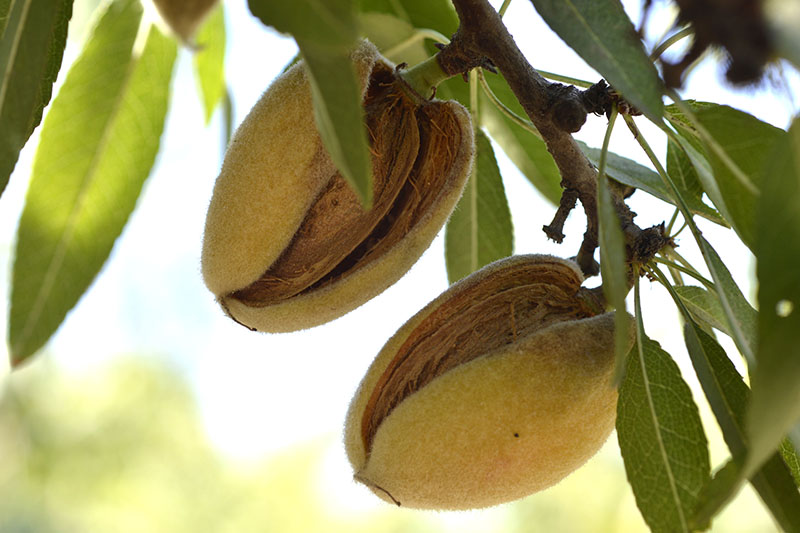
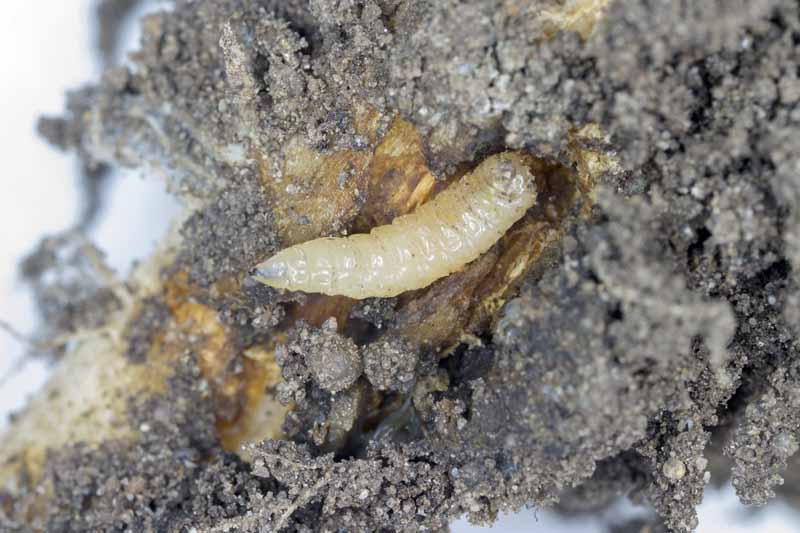
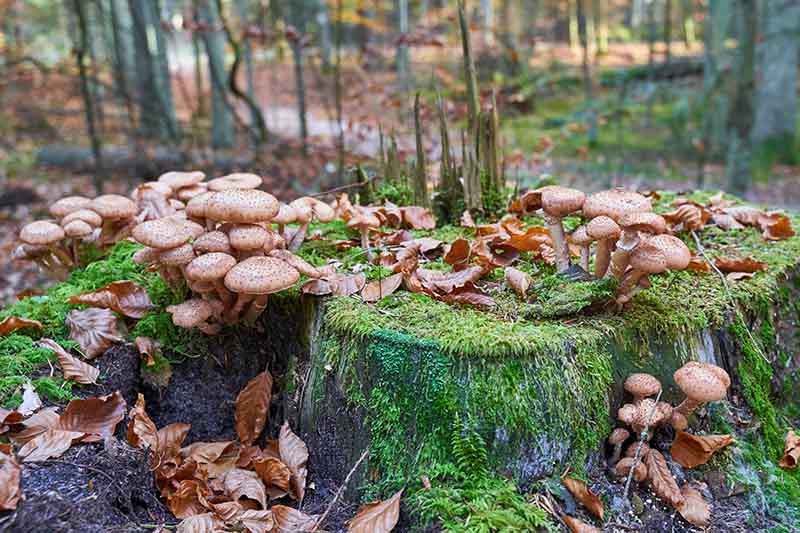
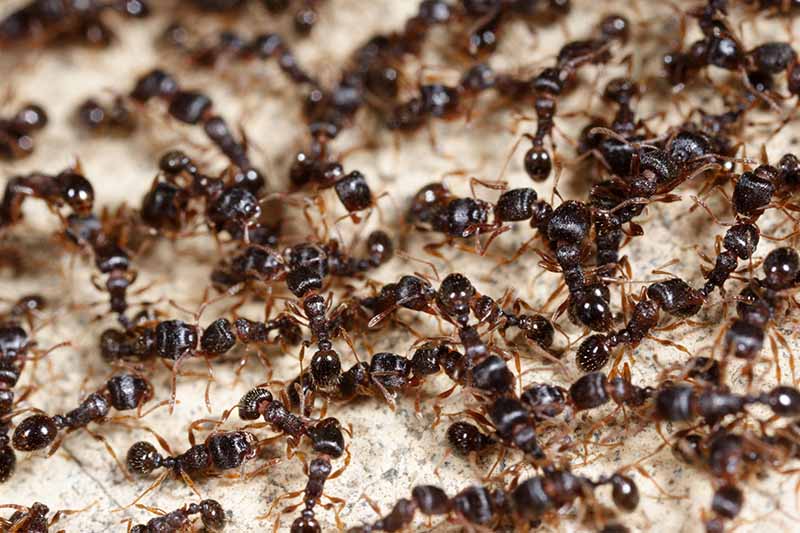
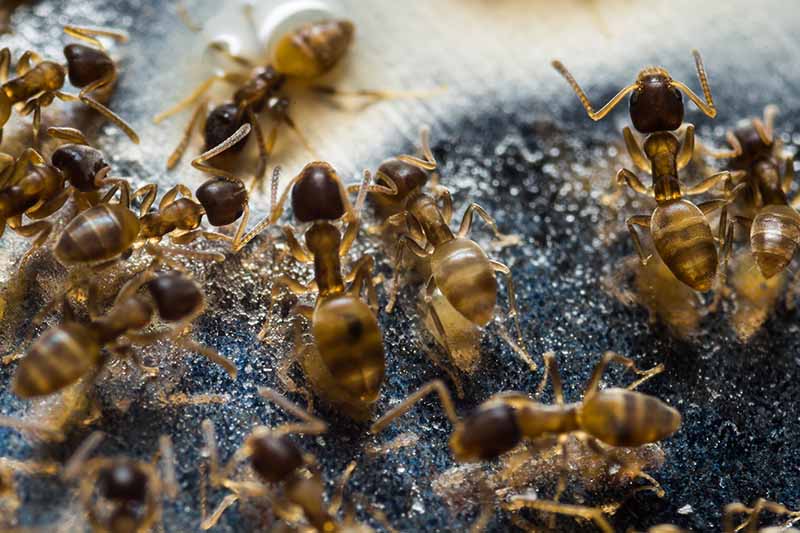
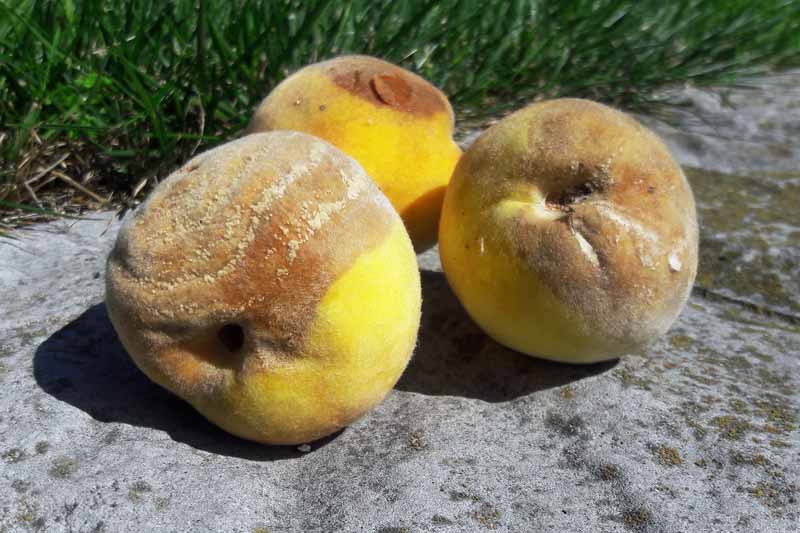
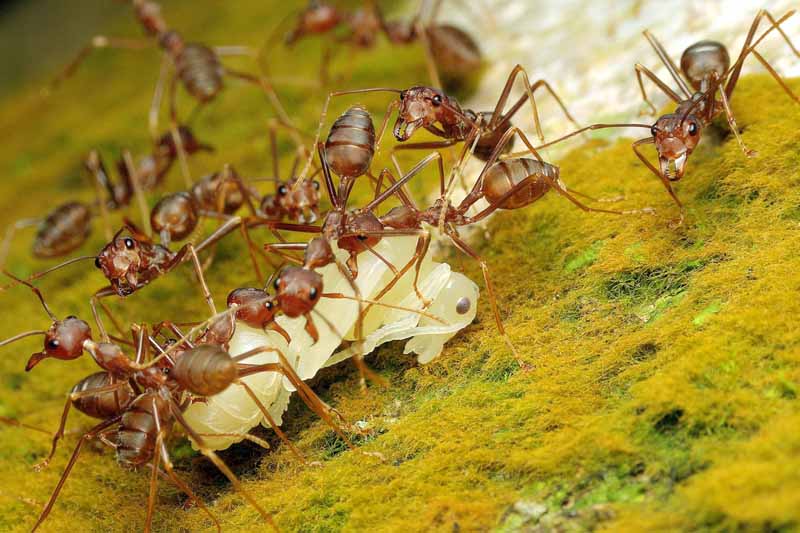
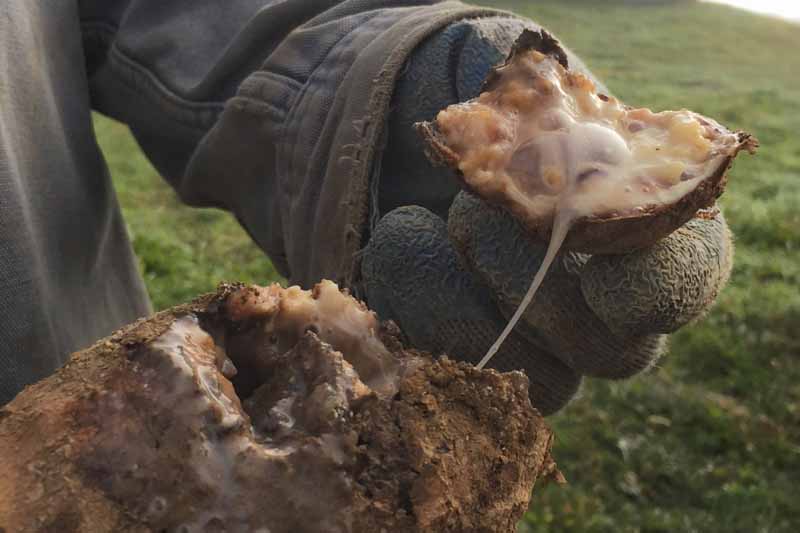
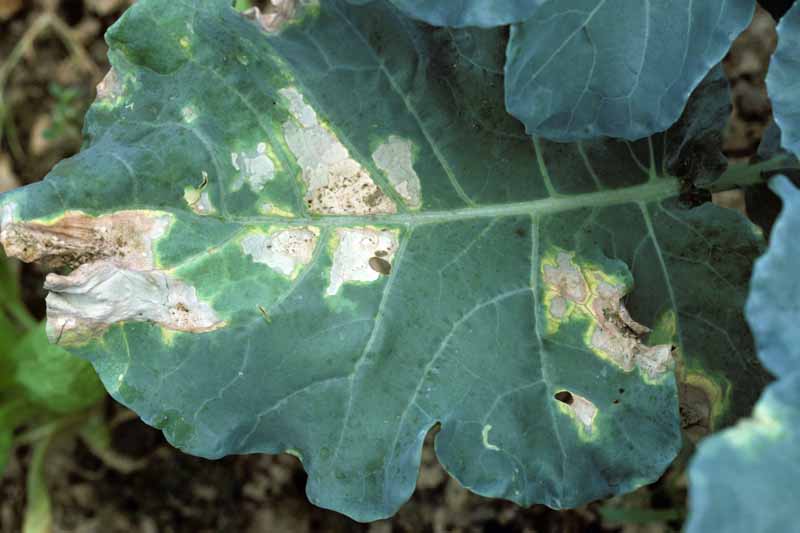
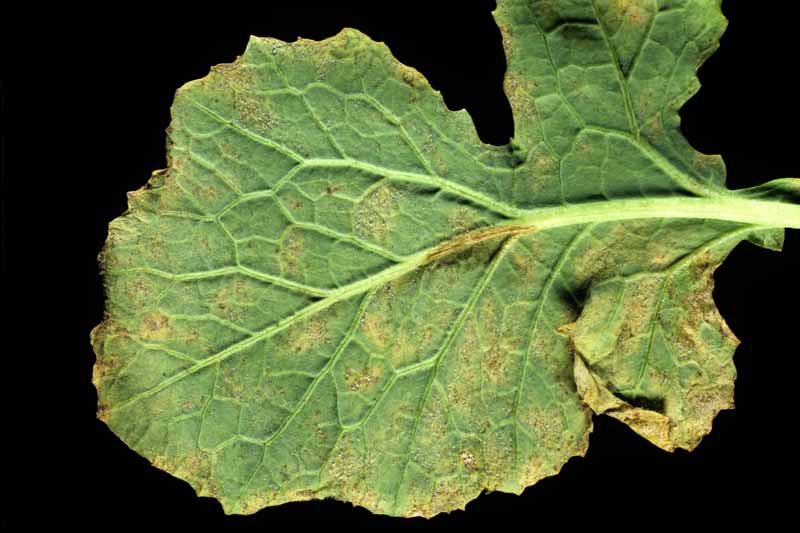
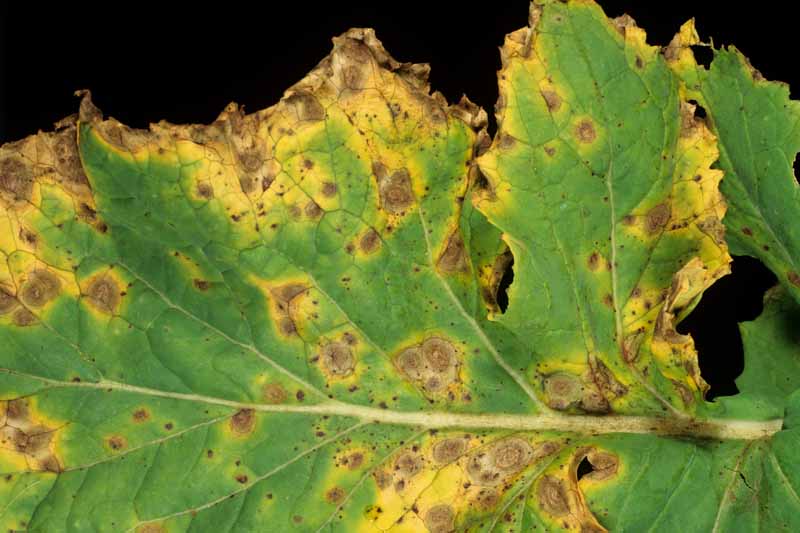
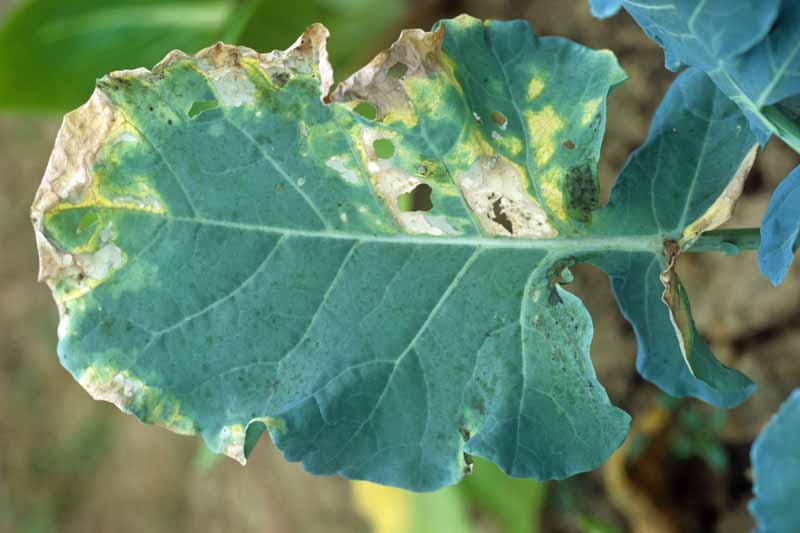
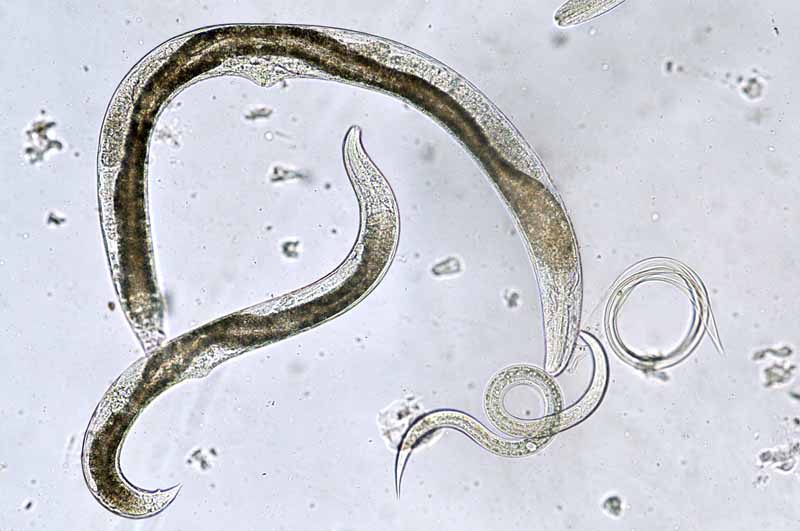
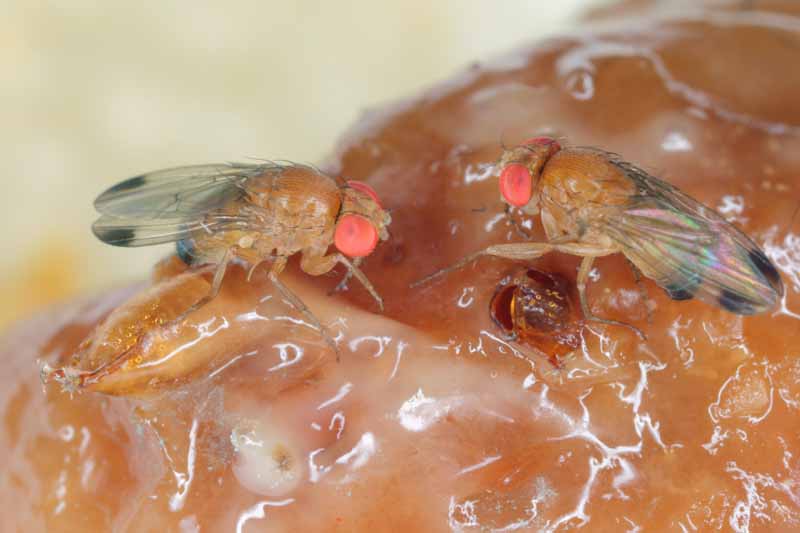
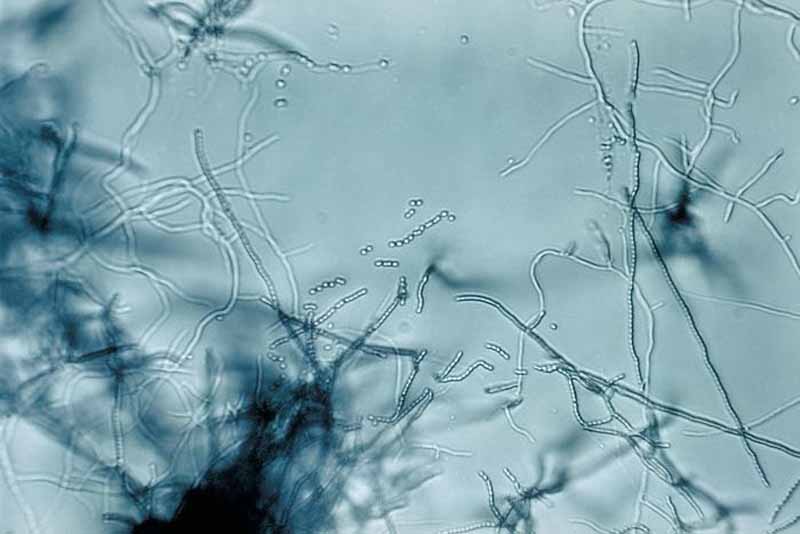
Pecan nuts that start to turn black and fall off the tree may be suffering from stem end blight. This fungal disease is spread by insects feeding on your trees and can cause severe damage to your crop. Fungicide treatment may be necessary if your trees are infected. Learn how to identify and treat this serious disease.